Description
This course covers the basics of federal tax preparation. The student will learn how the American Tax System began, how to interview the taxpayer to determine what filing status they should use and what tax credits the taxpayer may qualify for.
Objectives
At the end of this course, the student will be able to do the following:
- Explain how a nonrefundable credit affects the taxpayer’s tax liability.
- Recognize what is professional responsibility in tax preparation.
- Realize what the tax preparer’s responsibilities are to the taxpayer.
Field of Study: Federal Tax Law 8 Hours and Behavioral Ethics 2 Hours
Course Level: Basic
Prerequisite: General tax preparation knowledge is required
Delivery Method: Self-Study
Expiration Date to earn CEs: June 31, 2026.
This course does not qualify for California Continuing Education hours
Self Study
Learn at your own pace, read or watch the lessons, pass the exams.
Mobile Friendly
Learn on your phone, tablet, or computer.
Bilingual
All our courses are available in English y español.
Career Paths
No matter where you’re at in your career, we have courses for you.
Simple Learner Experiences
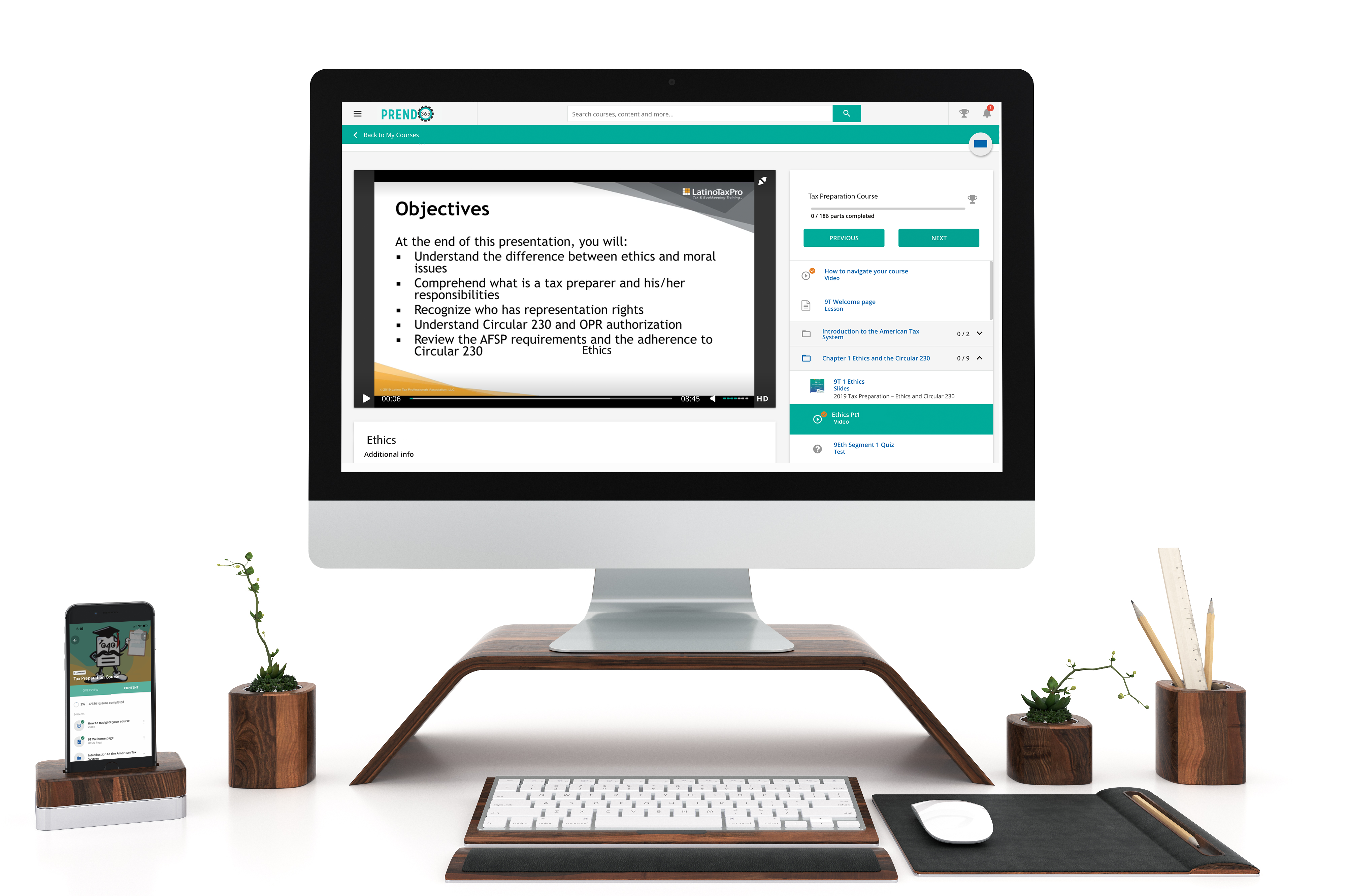
Prendo365 gives you access to your course anytime, anywhere, on desktop, tablet, or mobile device. You're able to easily navigate through your course and receive your certificate of completion.
Why choose us
Over 35+ years tax preparation experience
We know what tax preparers need to succeed in their office
7+ EA’s and tax preparers on staff
Our team does extensive research to ensure you receive the best education
Bilingual live support
Having technical issues? We're ready to help you get started and complete your course.